PARAGRAPH PAGE
F.1 GENERAL 507F.1.1 Scope. 507F.1.2 Applicability. 507F.2 APPLICABLE DOCUMENTS 507F.2.1 General. 507F.2.2 Government documents. 507F.2.2.1 Specifications, standards, and handbooks. 507F.2.2.2 Other Government documents, drawings, and publications. 508F.3 DEFINITIONS 508F.3.1 Standard definitions and acronyms. 508F.3.2 Abbreviations and acronyms. 508F.3.3 Operating parameters. 508F.4 GENERAL REQUIREMENTS 509F.4.1 Overview. 509F.4.2 Hop sets. 509F.4.3 System performance requirements. 510F.4.3.1 Linking probability: link before hopping. 510F.4.3.2 Linking probability: link while hopping. 510F.4.3.3 Occupancy detection: link before hopping. 510F.4.3.3 Occupancy detection: link while hopping. 511F.5 DETAILED REQUIREMENTS 511F.5.1 Linking before hopping. 511F.5.2 Linking while hopping. 511F.5.2.1 Hopping synchronous slot duration. 512F.5.2.2 Hopping synchronous dwell structure. 512F.5.2.3 Hopping PDU transmission. 512F.5.2.3.1 Hopping PDU transmit level control sequence. 512F.5.2.3.2 Hopping 3G-ALE PDU transmission during data time. 512F.5.2.3.3 Hopping transmission of other PDUs during data time. 513F.6 NOTES 513
TABLE F-I. Modes of operation. 509TABLE F-II. Linking probability requirements for linking while hopping (3 kHz SNR dB). 510TABLE F-III. Occupancy detection requirements for linking while hopping (3 kHz SNR dB). 511
FIGURE F-1. Hopping PDU transmission. 512
This appendix contains the requirements for implementation of
third generation (3G) HF link automation when frequency hopping
is used in anti-jam and anti-interference applications.
Frequency hopping operation with 3G HF link automation may not
be required for some users of HF radio systems. However, if the
user has a requirement for the features and functions described
herein, they shall be implemented in accordance with the technical
parameters specified in this appendix.
The documents listed in this section are specified in F.3, F.4
and F.5 of this appendix. This section does not include documents
cited in other sections of this standard or recommended for additional
information or as examples. While every effort has been made
to ensure the completeness of this list, document users are cautioned
that they must meet all specified requirements documents cited
in F.3, F.4 and F.5 of this appendix, whether or not they are
listed here.
The following specifications, standards, and handbooks form a
part of this document to the extent specified herein. Unless
otherwise specified, the issues of these documents are those listed
in the issue of the Department of Defense Index of Specifications
and Standards (DODISS) and supplement thereto, cited in the solicitation.
| STANDARDS | ||||
| FEDERAL | ||||
| FED-STD-1037 | Telecommunications: Glossary of
Telecommunications Terms | |||
| MILITARY | ||||
| MIL-STD-188-148 | (S) Interoperability Standard for Anti-Jam (AJ) Communications in the High Frequency Band 2 - 30 megahertz (MHz) (U) | |||
(Unless otherwise indicated, copies of the above specifications,
standards, and handbooks are available from the Standardization
Document Order Desk, 700 Robbins Ave. Building 4D, Philadelphia,
PA 19111-5094.)
The following other Government documents, drawings, and publications
form a part of this document to the extent specified herein.
Unless otherwise specified, the issues are those cited in the
solicitation.
| NTIA Report 98-348 | Software Implementation of a Wideband HF Channel Transfer Function |
(Applications for copies should be addressed to the U.S. Department
of Commerce, NTIA, Room 4890, 14th and Constitution Ave. N.W.,
Washington, DC 20230.)
None.
The abbreviations and acronyms used in this document are defined
below. Those listed in the current edition of FED-STD-1037 have
been included for the convenience of the reader.
| 3G | third generation | |
| AJ | Anti-Jam |
| ALE | Automatic Link Establishment | ||
| ALM | Automatic Link Maintenance | ||
| AWGN | additive white Gaussian noise | ||
| DODISS | Department of Defense Index of Specifications and Standards | ||
| HF | high frequency | ||
| kHz | kiloHertz | ||
| MHz | megahertz | |
| PDU | Protocol Data Unit |
The operating parameters used in this appendix are collected here
for the convenience of the reader.
| Symbol | Parameter Name | Default Value |
| Tsym | PSK symbol time | 1/2400 s _ 417 µs |
| Tbit | 32 Tsym; quantum of 3G PSK signaling | ~13.333 ms |
| Tprop | Maximum propagation delay among network members | 70 ms |
| Thop | Duration of hopping dwell | * |
| Tguard | Guard time at hop boundary for radio tuning | * |
| Tdata | Portion of hopping dwell used for data transmission (Thop - Tguard) | * |
| Tdisc | Maximum discrepancy among synchronized, hopping radios | * |
| Tslot | Duration of slot in synchronous mode 3G ALE | * |
| Nbph | Number of data bits sent per hop | * |
| Hbw0 | Number of hops necessary to send a 3G ALE PDU while hopping | * |
| C | Number of calling hop sets scanned by radio that links while hopping | |
| * depends on specific hopping scheme in use | ||
Systems employing both 3G HF link automation (see Appendix C)
and frequency hopping may operate in any of the following five
modes listed in table F-I.
| Mode | Hopping Mode | Linking Mode | Scanning Mode |
| 1A | MIL-STD-188-148 | Link before hopping | Async |
| 1B | MIL-STD-188-148 | Link before hopping | Sync |
| 2 | MIL-STD-188-148 | Link while hopping | Sync |
| 3A | Army enhanced | Link before hopping | Async |
| 3B | Army enhanced | Link before hopping | Sync |
An ordered list of frequencies, along with timing specifications
that determine when each frequency is used, is termed a hop set.
When 3G protocols are used in a frequency-hopping network, hop
sets take the place of channels. Thus, in 3G systems that support
frequency hopping, the channel table specified in C.4.11.3 Channel
table shall be extended to store a hop set specification in each
entry, and channel numbers in 3G automatic link establishment
(ALE) and 3G automatic link maintenance (ALM) protocol data units
(PDUs) shall refer to hop sets.
When linking before hopping (Mode 1A, 1B, 3A, or 3B), 3G ALE systems
shall meet or exceed the linking probability requirements of C.4.6.1.1
Linking probability and the appropriate sub-paragraph for linking
in synchronous or asynchronous mode.
When linking while hopping (Mode 2), 3G ALE systems shall meet or exceed the linking probability requirements of table F-II. The test procedure of A.4.2.3 shall be employed, with the following modifications:
When linking before hopping (Mode 1A, 1B, 3A, or 3B), 3G ALE systems
shall meet or exceed the occupancy detection requirements of C.4.6.1.2
Occupancy detection and the appropriate sub-paragraph for synchronous
or asynchronous operation.
3G ALE systems operating in link-while-hopping mode (Mode 2) shall
correctly recognize that a traffic hop set is occupied at least
as reliably as indicated in table C-II during the Listen portion
of Slot 0 (see F.5.2.2, Hopping synchronous dwell structure).
The test procedure of A.4.2.2 shall be used. Systems shall also
meet or exceed the requirements of
table F-III for detecting calling hop sets in use while listening
before calling during Slots 1 through 3. The probability of declaring
a hop set occupied when each hop dwell contains only additive
white Gaussian noise (AWGN) shall be less than 1percent.
| Waveform | AWGN 3 kHz SNR (dB) | Minimum Required Detection Probability |
| 2G-ALE | ||
| 3G-ALE (BW0) | ||
| 3G-HDL (BW2) | ||
| SSB Voice | ||
| MIL-STD-188-110 or | ||
| FED-STD-1052 PSK modem | ||
| STANAG 4285 PSK modem |
When 3G ALE systems link before hopping, the ALE protocols of
Appendix C shall be employed with the following modification:
hopping synchronization and startup shall occur at the point
in the respective protocol at which traffic startup would occur
in non-hopping operation. Traffic startup shall commence upon
completion of hopping startup.
When linking while hopping, a 3G ALE system shall operate in the modified synchronous mode specified below. The following timing parameters are used:
When the network hopping rate is such that an entire 3G-ALE PDU
can be sent during Tdata, the slot time Tslot
shall be equal to Thop. Otherwise, the 3G-ALE Tslot
shall be extended to the smallest integral multiple of Thop
greater than or equal to Tprop plus the time to send
an entire 3G-ALE PDU using the procedure specified in F.5.2.3
Hopping PDU transmission.
The dwell structure for 3G ALE while hopping shall comprise five slots, each of duration Tslot:
When any 3G PDU cannot be sent during a single hop, it shall be
spread over multiple hops as described below.
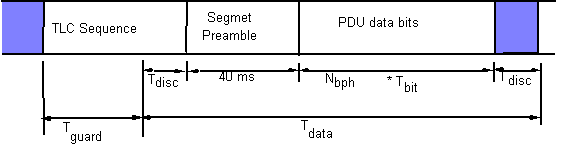
The transmit level control portion of a PDU shall be sent by the
controller to the transmitter during Tguard and the
first portion of Tdata, with symbols dropped from the
beginning of the sequence if necessary so that the end of the
Ttlc sequence shall occur at time Tdisc
after the end of the guard time (see figure F-1). Some of the
symbols may be dropped by the transmitter while it is changing
frequency.

When Tdata > TBW0 pre
+ TBW0 data + 2 Tdisc, the 3G-ALE
PDU shall be sent during a single hop, with the preamble beginning
immediately after the end of the Ttlc sequence.
Otherwise, the preamble and data portions of the 3G ALE PDU shall be split over multiple hops. The transmissions during each Thop shall be (a portion of) the Ttlc sequence as described above, followed immediately by a 40 ms (96 symbol) segment of the preamble, followed immediately by up to Nbph PDU data bits:
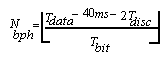
Transmissions should cease during the period from the final symbol
of the PDU data bits until the first symbol of the next Ttlc
sequence. This will reduce interference levels. The number of
hops required to send the 26 data bits that compose a 3G ALE PDU
is HBW0:
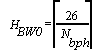
Preamble segments shall be sent in order in successive hops, with
the specified symbol sequence cycling back to the beginning if
necessary in the later hops. If the unused PDU data bit positions
in the final hop do not exceed Tprop, an extra hop
must be included in Tslot to allow for propagation
to all network stations.
The other 3G PDUs shall be sent similarly to the 3G ALE PDUs.
None.